Computer Fundamentals with C and Unix
(Data types)
Lecture 02: Dec. 17, 2022 Prof. K.R. Chowdhary : Professor of CS
Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved for formal publications. They may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor.
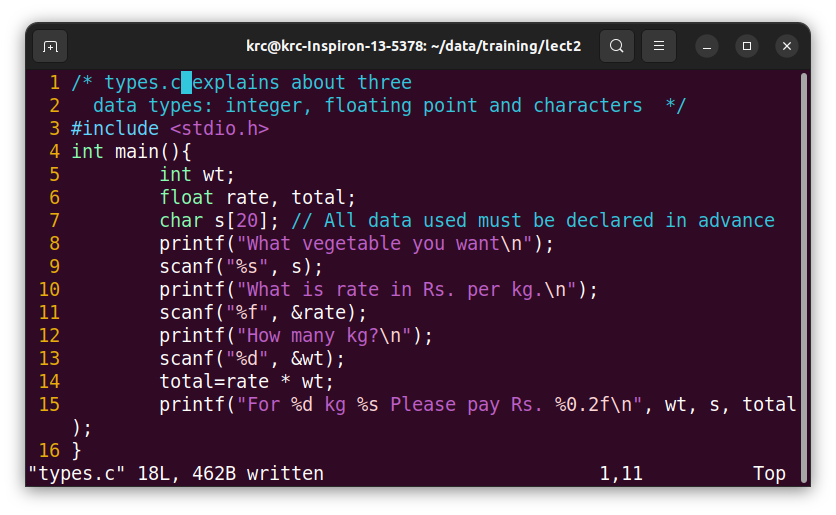
Through the program we do computations on data, which may be of various types depending on the requirements of the application. For ordinary arithmetic we need integers, for real life applications there are real numbers, called float, e.g., Rs. 30.5/kg onion, and the names are represented as character strings, and individual characters are are char types. The following example demonstrates this.
The above programs gives many things to learn:
the main() is a function, and the program in this are run first, always, in any C program. This function is run by the OS (operating system). When it is successfully run, it returns a code value to OS, e.g., 0 will be returned if it has successfully run, and other values, say -1 if there is some error of running it. So, the OS will come to know what has happened through that code. That is why there is “int” before main, to indicate that main returns an integer value.
Following to main there are always data declaration. That is, the names of data and their values if available. The values of these data may be available by assigning to these names (of data), or may be input from keyboard while the program runs, or these data may also come from other places, e.g., files, or network or internet.
Various data declared in this program are wt, which can be integer only, rate and total, which are float, e.g., 240.5, 20.124, etc. The third data is s, which is character, and its length is 20. So it is an array of 20 characters. None of the data is initialized in the program, and they will be assigned by input, while total will be assigned by calculation by multiplication operation.
The printf is a function. It as text string as one argument embedded with image of data items shown by %d, %f, %c, etc, with floating length or %5d, %0.2f, %s with specified length. These formats are for integer, real, character strings. The string in the printf is followed with data arguments or variable names. The format of printf we call as syntax of print statement.
The scanf is a function with two argument types: 1) data formats, like, %d, %f, %c, etc put under the quotes, and this is followed with memory locations where values shall be stored of the given data items or variables. This we call as syntax of scanf statement. If a variable is wt, then its memory location is &wt, similarly for rate variable it is &rate, etc. However, for the data which is array, e.g., character array, the start memory location where it is stored is the name of the array itself. For example, for “char s[10]”, the start location of its memory is s, or &s[0]. Both are equal and have same meaning.
You need to describe a C program code with comments inside the program itself. There are two types of comments:
Multiple line comment: Embed the comment between /* and */
Single line comment: // this is in single line
The program types.c we discussed above is a simple program, where statements of C are executed in sequential order and each one is executed once only. There is no loop to repeat any statement either there is any conditional statement to select a statement for execution.
The data declaration part is for restricting the size and type of data that can be stored in the variables. This binds the type with the variables, hence in the future statements in the program only that type of data can be assigned to that variable, else there will be error.
The errors in the program are checked during the compiling. The source program is types.c and the compiled program is a.out. We note that size of source program is only 328 bytes, while the size of compiled and linked program a.out is 16104 bytes. The latter is far bigger, because the for every statement in the source language (C here) there ar hundred of machine language statements. Imagine, if we are asked to write a program in machine language, it will be too tedious and time consuming process. So, let us thank to the people who wrote compilers, which have simplified the job for us, cheers to them !!
Remember that, in the informal talk, we are learning Linux1 also, but don’t be afraid, it will not be difficult. The Unix is OS for programmers, and there is lot to learn from Unix for CS.
The Unix has directory structure, i.e., tree of folders and files, with a root. Following are some commands:
pwd: print working directory
ls: list names of files and directories under current directory
ls -l: Long list of the same, with group id, user id, size, date, name, and number of links associated.
In the begin of ls -l’s every row, rwx rwx rwx are permissions for user, group and others, for read, write, and execute. The ”-” shows that permission is not granted. The first character as ”-” says that it is a file and when it is ”d”, it means it is directory.
Some of the common commands for file operations are:
| S.no. | Command | Description |
| 1. | $ cat hello.c | displays the contents of hello.c file |
| 2. | $ cp hello.c ok.c | copies first file into second |
| 3. | $ mv hello.c ok.c | renames the first as second file |
| 4. | $ more hello.c | displays hello.c page wise |
| 5. | $ head hello.c | displays top 10 lines of hello.c |
| 6. | $ tail hello.c | displays last 10 lines of hello.c |
| 7. | $ wc hello.c | displays number of lines, words and characters in hello.c |
| 8. | $ rm filename | removes the file, i.e., deletes it from the storage |
There are more data types in C:
short or short int: For integers that are -128 to o to +127 = (256 total), it occupies one byte
long int: It is for bigger integer, and occupies 4-bytes in RAM
double : it is float and occupies 8 bytes in memory
binary : it is one bit size
Octal: in octal format
Hexadecimal: It is 16 base number.
Smallest size memory you can allocate is one byte, and memory is always 8, 16, 32, 64 bytes sizes and no in between, in all the modern computers.
Different types of variables consume different amount of space in memory (i.e., Random Access Memory (RAM)) of the computer.
Short: 1 byte
Character: 1 byte
int : 2 bytes
long : 4 bytes
double: 8 bytes
long double: 16 bytes
Examples of bytes are: 0000 0000, 0000 0001, ..., 1111 1111. Note that each one is of fixed length 8 bits.
Though we can do computations using hexadecimal, octal, and binary as well as print the in their formats, but there are no data types like binary, octal and hexadecimal.
The syntax is name of grammatical rules of writing C program statements. Like, correct syntax of
a sentence is “Student is in School”, and not “School in is student”. Similarly, correct syntax
are:
basic = 10000; da = 5000; hra = 5500;
pay = basic + da + hra;
printf(“%f\n”, pay);
and not
10000=basic; 5000=da; ....
printf(pay);
Semantic is the meaning associated with a statement, say:
pay = basic + da + hra;
means pick up the data corresponding to variables basic, da, hra from the respective memory locations, bring them into cpu, do addition, and store the result in the memory location designated by variable “pay”.
The compiler performs mostly the syntax checking, while semantics is checked (mostly) during the running of the program.