Computer Fundamentals with C and Unix
(Recursive Functions and Pointers)
Lecture 9: Jan. 11, 2023 Prof. K.R. Chowdhary : Professor of CS
Disclaimer: These notes have not been subjected to the usual scrutiny reserved for formal publications. They may be distributed outside this class only with the permission of the Instructor.
Functions in C are the basic building blocks of a C program. A function is a set of statements enclosed within curly brackets () that take inputs, do the computation, and provide the resultant output. You can call a function multiple times, thereby allowing reusability and modularity in C programming. It means that instead of writing the same code again and again for different arguments, you can simply enclose the code and make it a function and then call it multiple times by merely passing the various arguments.
We need functions in C programming and even in other programming languages due to the numerous advantages they provide to the developer. Some of the key benefits of using functions are:
Enables reusability and reduces redundancy
Makes a code modular
Provides abstraction functionality
The program becomes easy to understand and manage
Breaks an extensive program into smaller and simpler pieces
There are more important facts about the function sin C language Programming:
Every program in C has a function. Even if you do not use a library or user-defined function, you will have to use the main function. The main function is the program’s entry point, as that is where the compiler will start executing the code.
Even if a function does not return a value, it has a return type. If a return value is provided, the return type is the data type of the value. But if there is no return value, then the void is the return type of the function.
C functions cannot return array and function types. However, you can easily overcome this limitation with the use of pointers.
While in C++, void func() and void func(void) mean the same; it is not the case with C programming. In C, a function declared without any parameter list can be called with any number of parameters. Hence, it is advisable to declare a function as void func(void) and not void func() if you want to call a function without any parameter.
If you call a function before the declaration, the C compiler will by default consider the return type to be int and show an error if the data type of the return value is anything except int.
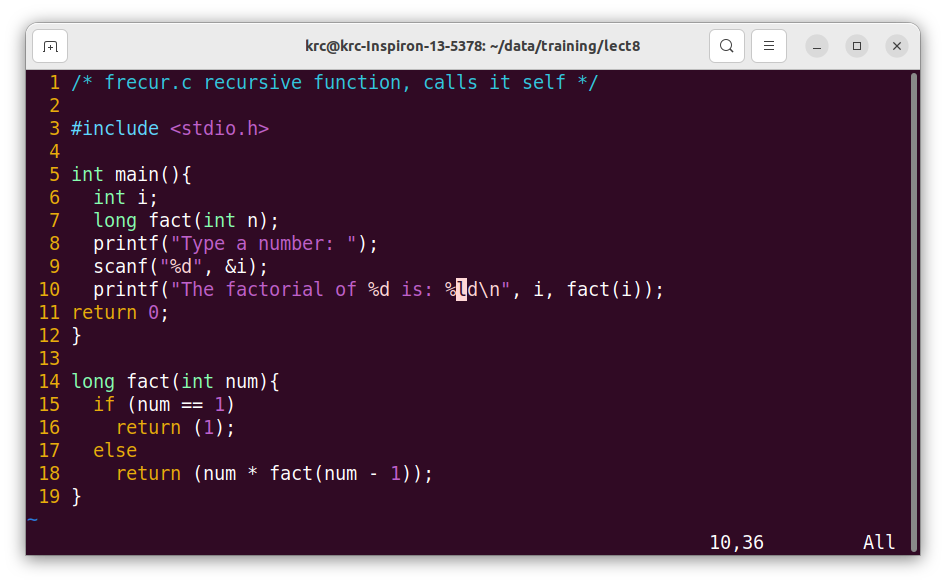
Functions in C programming are recursive if they can call themselves until the exit condition is satisfied. If a function allows you to call itself within the definition in a C program, it is a recursive function. These functions run by stacking the calls until the exit condition is met and the flow of the program exits the function. Suppose you want to find the factorial of a number in C; you can use a recursive function to get the result. Here’s an example to find the factorial of 8.
#include <stdio.h>
int fact(int num);
int main(){
int i = 8;
printf("The factorial of %d is: %d\n", i, fact(i));
return 0;
}
int fact(int num){
if (num == 1)
// Exiting condition
return (1);
else
return (num * fact(num - 1));
}
The Fig. 9.1 shows a recursive function, that computes the factorial of a given number. To take large numbers, the type of that variable as well as the function have been declared as long integers.
The Fig. 9.2 shows the running of the program mentioned above that calls the recursive function for factorial computation.